C360 Self Serve
Overview
Role
Product Design, User Research
What is C360?
C360’s mission as Intuit’s customer data portal is to provide access to high-quality customer data to personalize product experiences, marketing, and customer care. Developers, Analysts and Data Scientists within Intuit can onboard new data and insights to the central data repository, enabling real-time data-driven personalized experiences, ultimately increasing the value end customers get out of Intuit’s products.
Personas: Data Scientists, Data Analysts, Developers
Why is it important?
C360 data is what enables teams across Intuit to create personalized experiences for end customers. According to Accenture, 91% of consumers are more likely to engage with brands who recognize, remember, and provide relevant offers and recommendations.
Use cases:
Can help Credit Karma match people looking to save money on their mortgage with just the right refinance opportunity
Can help marketers maximize the signup funnel for a specific user segment
Virtual Experts can use the data to know the likelihood that a TT user will abandon the experience
Goals
Speed: Marketing teams need quick access to customer data in order to execute on campaigns and strategy with agility. The faster data can be onboarded, the faster we can deliver personalized experiences to end users.
At the start of FY20, data onboarding to C360 took an average of 40 days (8 weeks!). The goal was to get this number down to 1 day by FY22 Q4.Quality: Data coming from C360 needs to be clean and high quality in order to be used as a single source of truth for downstream destinations.
Problem to solve for
“I am an Intuit employee and need to onboard new data attributes to C360, but the process is confusing and long. I can’t onboard without going through many rounds of back-and-forth with support, which makes me feel frustrated and blocked on my other work.”
Solution
To simplify the data onboarding process, data parsing and C360 project teams were introduced. Allowing users to drag and drop their data to autofill fields was much faster compared to manual entry, and project teams allowed users to work together with their existing teammates to collaboratively fill out onboarding requests.
Research and Pain Points
I collaborated with my PM partner to interview a total of 12 individuals coming from different backgrounds, including Data Analysts, Engineers, Marketing Managers, Business Analysts, and PMs.
Research objectives
Discover users’ mental models surrounding data attribute upload
Understand pain points - where are users getting stuck in the flow?
Learn about users’ ideal experience so that it can be converted into actionable next steps
Research findings
Following the 12 interviews, I analyzed the data through the affinity diagramming process, and shared out the insights with the team, including the PM, Developer Manager and Developers.
Lack of editing flexibility: when uploading new user data (called “attributes”), users needed to fill out metadata relating to each attribute manually.For users coming in with 10-20 attributes they wanted to batch onboard, this process became very tedious.
Lack of key knowledge: knowledge was often limited to only a few people on each team, creating bottlenecks in the onboarding process. Users had to go back and forth within their own team to get information required in the self-serve flow. This was exacerbated by the fact that C360 onboarding requests were not shareable, so users had to spend time coordinating group calls to fill out the self-serve request collectively
Our users’ journey map
Two major pain points
I discovered a couple pain points preventing users from onboarding data as quickly as they wanted, but two major ones stood out:
Design Updates
1. Enabling data parsing for accelerated data onboarding
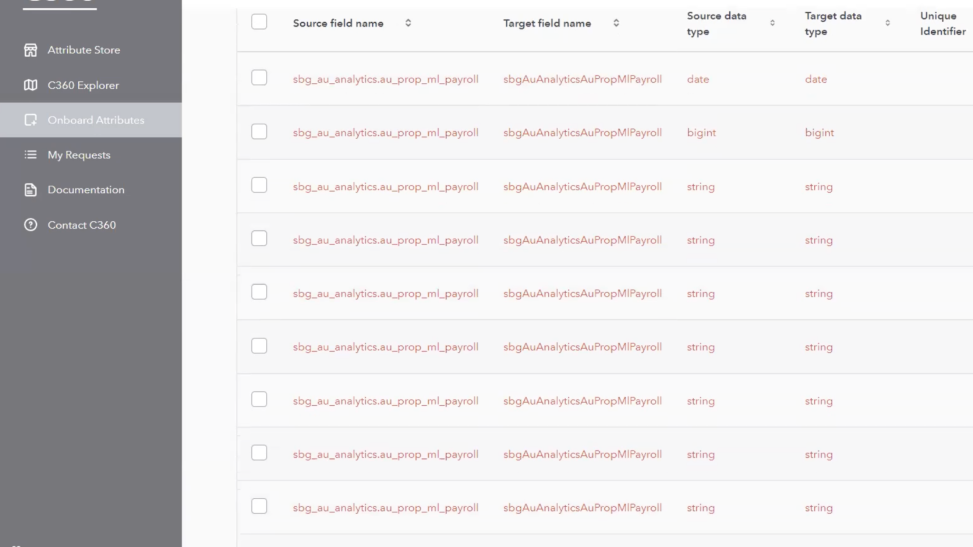
Users had two options for the data attribute details screen - manually fill things in line-by-line, or upload a spreadsheet with specific formatting.
Both of these methods led to errors frequently; the screenshot to the right shows what happened to one user when they uploaded a spreadsheet with incorrect formatting. Errors appeared in every line, which would need to be fixed manually.
How might we make our attribute editing process more efficient and less prone to human error?
Add data parsing in the form of a file drag-and-drop so we can detect attributes and autofill metadata directly from the data source (payload). This saves users time and decreases the likelihood of errors occurring down the line
Redesign the manual editing process so that users can edit without needing to drill down into each row individually. This way users can add in anything the data parsing misses
Users can drag and drop a .json file of their data payload directly in the blue area
2. Designing a “teams” system for shared access
In most cases, users needed to rely on their teammates to help them with certain pieces of information. Users would get together with their team on Zoom calls and compile information on a spreadsheet before onboarding, adding an extra step to the process. Some users also explained that they didn’t feel confident submitting the onboarding request without being able to have a teammate checking over the fields first.
How might we help our users feel more prepared, confident, and supported using C360 self-serve?
Constraints: It wasn’t possible to reduce the complexity of the onboarding requirements, because from a technical standpoint all of these pieces were required to maintain clean, well-organized data.
Users naturally gravitated towards collaboration, so to align with our users’ mental mode, we decided to add the concept of “teams” into the self-serve platform.
With the addition of teams, users can create teams directly in C360 self-serve.
A secondary tab on the same page allows users to paste a code snippet of the payload instead
Data parsing is able to pick up on the source name, source path, and data type
Users can share with teammates through email and assign them to different roles.
When users encounter fields they need help with, they can share the request with a teammate
Once the payload files are uploaded, C360 starts parsing for attribute data
For any additional information such as individual descriptions, users can still edit manually
One user can be in multiple different teams. This lets the user organize their onboarding requests.
The teammate receives a notification in their email with a message and link to the request
Outcomes and Learnings
Onboarding time reduced from weeks to <24 hours
95% of all use cases covered by self-serve experience
Self-serve adoption rate of 100% for all supported use cases
The design and development updates we made following user research helped users onboard data to C360 self-serve more efficiently, and decreased the number of tickets coming into support. I had one main learning from this project:
The user journey begins before the user first starts interacting with the product. Through user interviews, I discovered that many users were doing extra work by preparing an information spreadsheet before even attempting to use C360 self-serve. Making this discovery helped me understand the gaps in our experience, and how to better support our users.
As of FY24, C360 is exploring further integration with other data platforms within Intuit to empower more teams across Intuit to leverage customer data and create personalized customer experiences.